
Discovering the intricate workings of your dog’s behavior is critical to fostering a harmonious bond with your furry companion. In this post, we’ll dive into a captivating aspect of territorial aggression in dogs.
This intriguing behavior can perplex pet owners, but fear not! We’ll unravel its reasons and explore practical strategies to tackle and manage it confidently. Let’s embark on this enlightening journey together!
The Nature of Territorial Aggression: A Natural Instinct
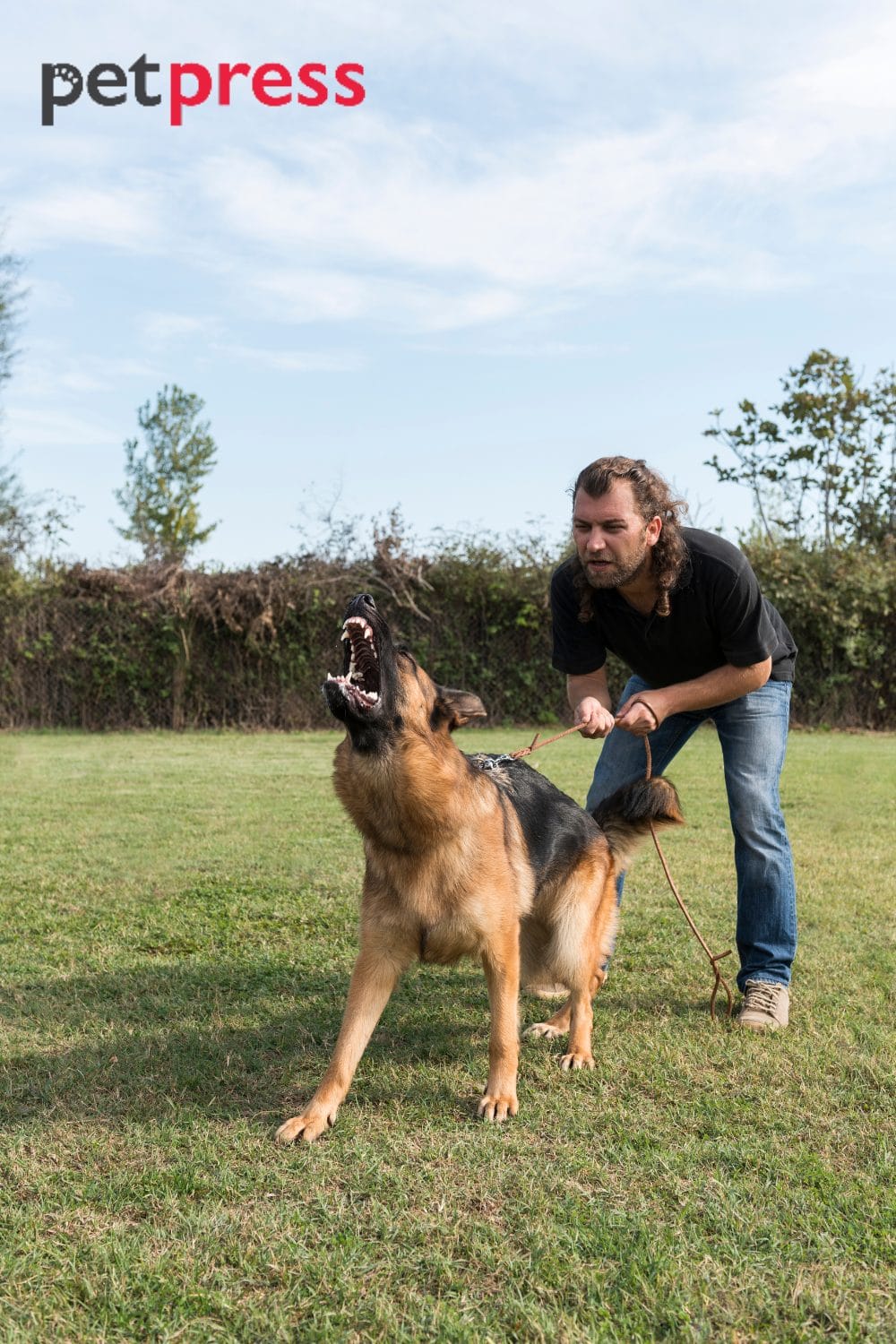
Territorial aggression in dogs is an instinct rooted in their evolutionary history. It stems from their ancestral connection to wolves, known for their territorial behavior. It can manifest as aggressive behavior towards intruders, humans, and other animals, threatening their perceived space.
While domestication has influenced their behavior, dogs may still exhibit territorial aggression. Barking, growling, or lunging can be their way of asserting dominance, but it doesn’t necessarily make them bad or ill-tempered. Instead, it is a natural response to what they perceive as a threat to their territory.
Various factors, such as genetics, upbringing, experiences, and socialization, can contribute to territorial aggression in dogs. The intensity of this behavior varies depending on the dog’s temperament, past experiences, and how they perceive potential threats.
Understanding the nature of territorial aggression allows dog owners to address the issue with empathy, patience, and effective training techniques. With consistent training, it is possible to modify and manage territorial aggression, leading to a confident and balanced canine companion.
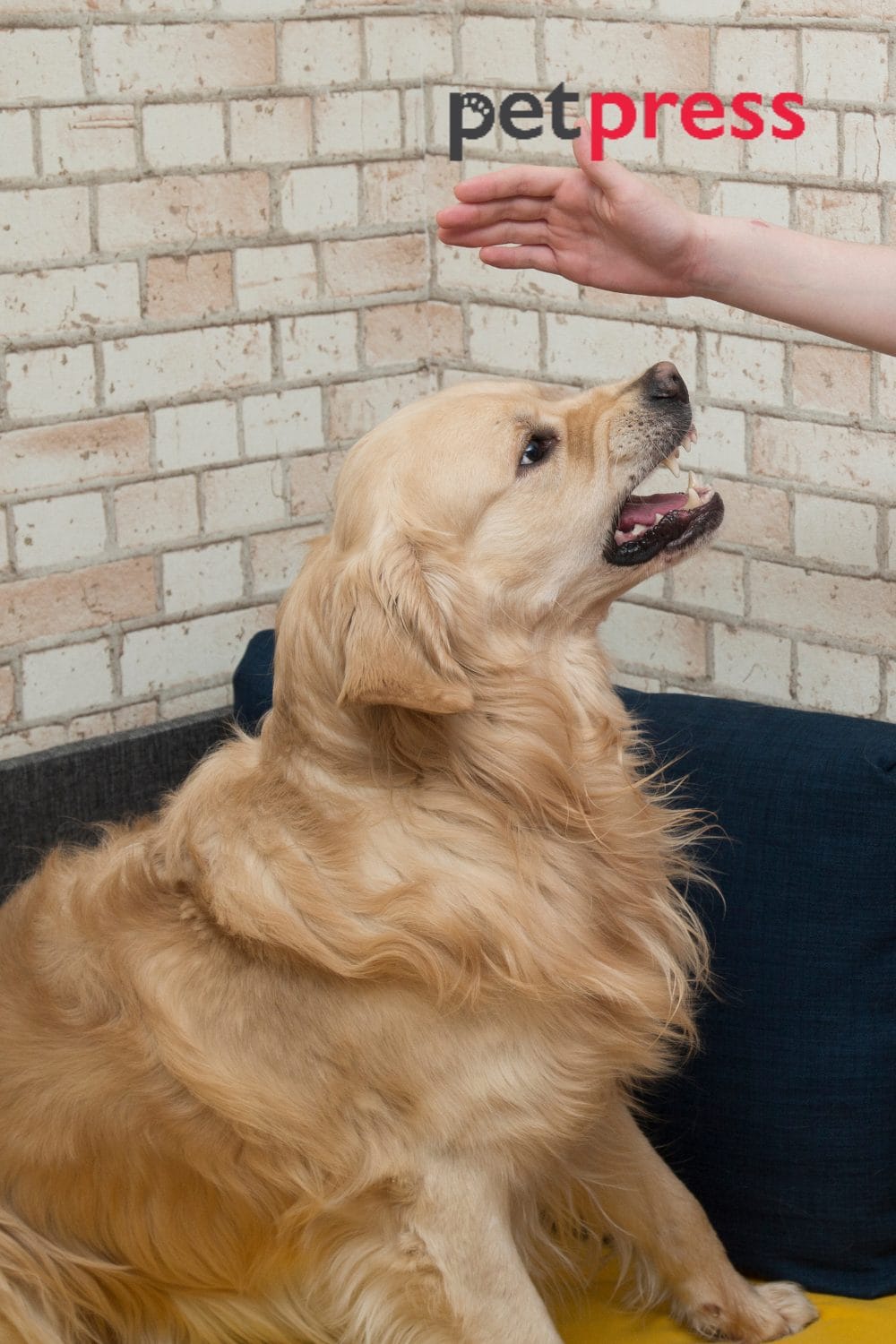

Recognizing Signs of Territorial Aggression: Key Indicators to Watch For
Identifying the signs of territorial aggression early on can help you proactively manage your dog’s behavior. Common indicators include barking, growling, lunging, and even biting when someone or something enters their territory. By recognizing these warning signs, you can intervene and redirect their behavior before it escalates.
- Excessive Barking or Growling: When someone or something enters their perceived space, dogs may emit deep, menacing growls or high-pitched, intense barks to ward off the perceived threat.
- Protective Stance and Body Language: Dogs displaying territorial aggression often assume a protective stance by stiffening their body, raising their hackles, and positioning themselves between the perceived intruder and their territory. They may also display dominance and a readiness to defend their territory.
- Lunging or Charging: Territorial dogs may lunge or charge towards the perceived intruder when feeling threatened. This aggressive behavior intimidates and establishes dominance, causing the intruder to retreat from their territory.
- Snapping or Biting: In extreme cases, territorial aggression can escalate to snapping or biting. Dogs may resort to this behavior as a last-ditch effort to protect their territory or themselves. It is crucial to address territorial aggression before it reaches this level of intensity.
- Resource-guarding: Dogs exhibiting territorial aggression may also display resource-guarding behavior. They may fiercely protect their food bowls, toys, or personal belongings, growling or snapping if someone tries to approach or take them away.
Not all dogs will show every sign mentioned above. Some might display a mix of these behaviors, while others only show a few. Also, the intensity of these signs can vary from mild to severe, depending on the dog.
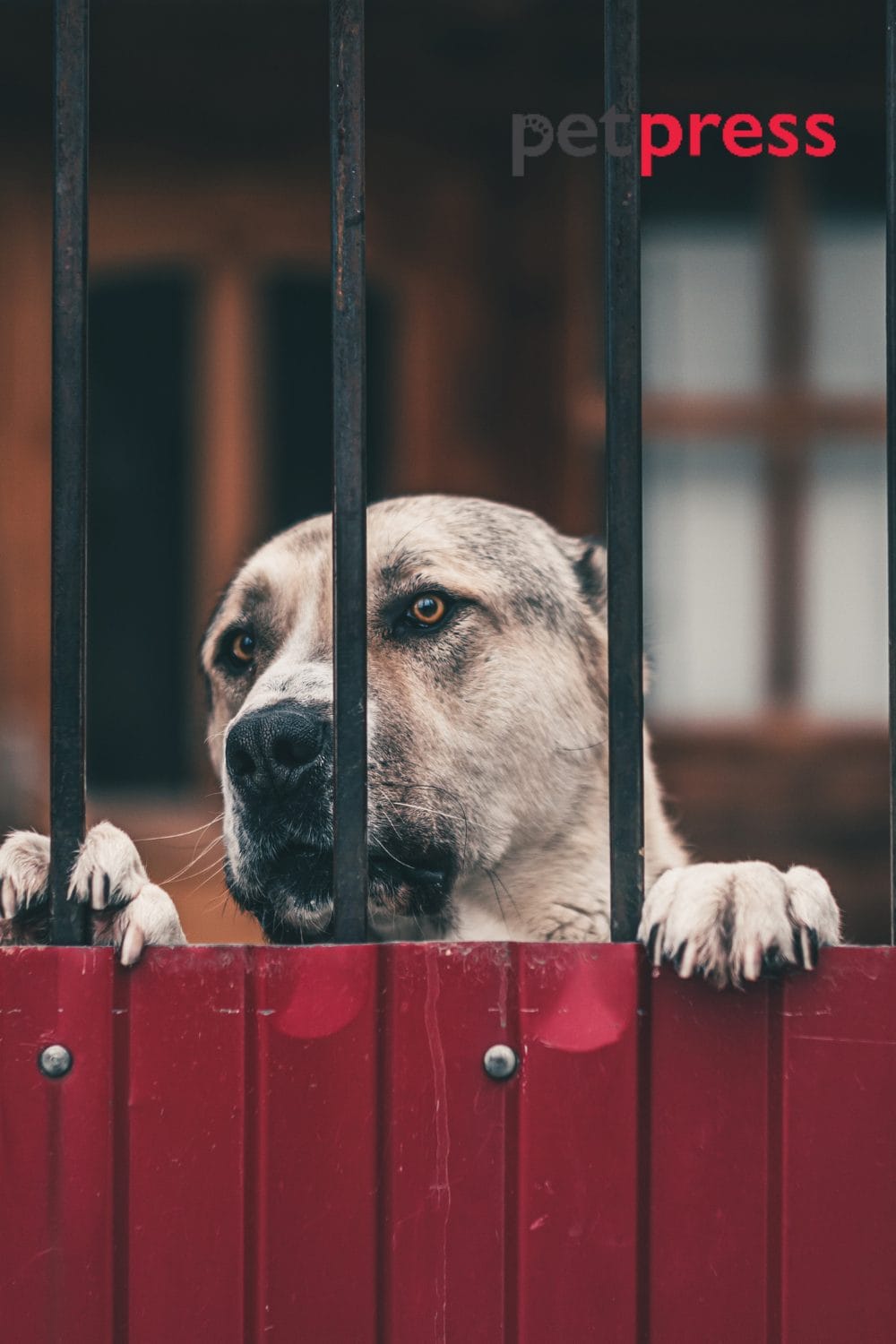

Factors Influencing Territorial Aggression in Dogs
Various factors, such as dog breed can influence territorial aggression in dogs, each contributing to the development and intensity of this behavior. By understanding these, dog owners can gain insights to implement appropriate strategies to address and manage territorial aggression.
Here are some common factors to consider:
Genetics and Breed Predisposition:
Certain dog breeds have a greater tendency for territorial aggression, like German Shepherds, Rottweilers, and Doberman Pinschers, which are influenced by their genetic makeup.
However, let’s remember that genetics aren’t the only determining factor. A dog’s behavior is also influenced by their temperament, adding to the fascinating complexity of canine companions.
Lack of Proper Socialization
Insufficient socialization during critical developmental stages can contribute to territorial aggression. Dogs not exposed to various people, animals, and environments may perceive unfamiliar individuals or animals as threats to their territory.
Traumatic Experiences or Fear:
Dogs that have gone through traumatic experiences, such as abuse or attacks, may develop territorial aggression as a defensive response. Fear can trigger aggressive behavior as a means of self-protection or an attempt to prevent similar incidents from happening again.
Guarding Resources:
Resource guarding is a behavior where dogs protect their possessions, such as food, toys, or resting spots. This possessive behavior can extend to guarding their territory.
Dogs exhibiting territorial aggression may view their living space as a valuable resource that needs protection, leading to defensive or aggressive behavior towards intruders.
Protective Instincts:
Dogs possess a natural inclination to protect their owners and family members. As a manifestation of their strong protective instinct, certain dogs may exhibit territorial aggression, viewing any perceived threat to their loved ones as a challenge to their domain.
Lack of Boundaries or Consistent Rules:
Dogs thrive on structure and clear boundaries. Consistent enforcement of rules or a lack of clear boundaries within the household can lead to confusion and stress for the dog. This can contribute to territorial aggression, as dogs must establish control and protect their space.
By addressing the underlying causes of territorial aggression and implementing appropriate training techniques, you can work towards minimizing and managing this behavior, leading to a calmer and more balanced canine companion.
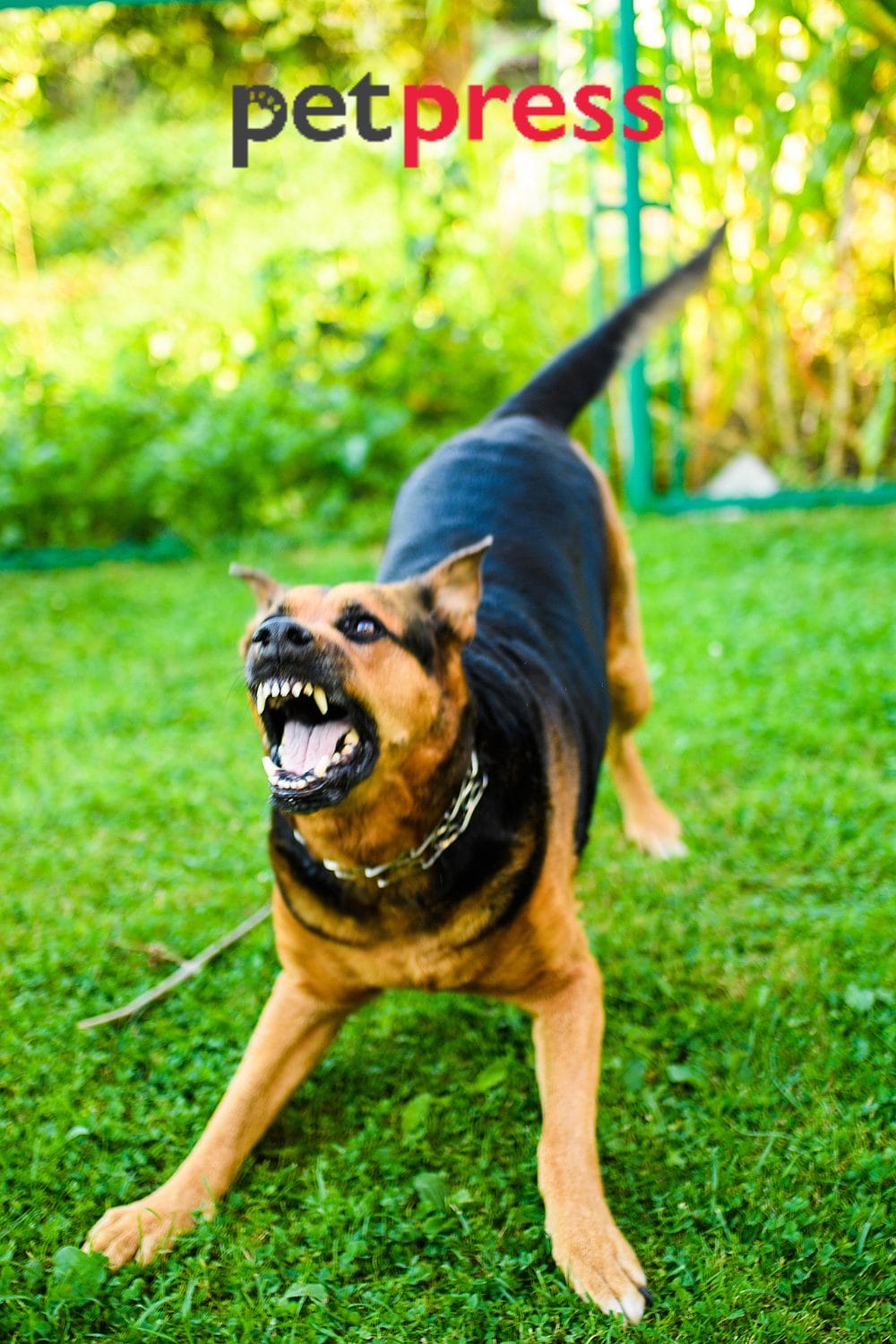

Positive Reinforcement Training for Territorial Aggression
Positive reinforcement training is a proven method to modify territorial behavior in dogs. By rewarding desired behaviors and redirecting their attention away from potential triggers, you can gradually reduce their aggression and encourage more appropriate responses. Patience and consistency are essential when using this training approach.
Creating a Safe and Balanced Environment
Creating a safe and balanced environment is essential in managing territorial aggression. This includes proper socialization from an early age, providing sufficient mental and physical stimulation, ensuring a comfortable living space, and implementing consistent boundaries. You can minimize the risk of territorial aggression by addressing your dog’s underlying needs.
- 1. Boundary Bliss: Establish clear boundaries within your home, guiding your dog’s behavior with consistency and love. A structured environment sets the stage for a safe and balanced space.
- 2. Enrichment Extravaganza: Keep your furry friend mentally and physically stimulated with interactive toys, puzzles, and engaging activities. A fulfilled pup is a happy pup!
- 3. Socialization Sensation: Introduce your dog to different people, animals, and environments from a young age. Socialization paves the way for a confident and well-adjusted puppy.
- 4. Routine Rendezvous: Dogs thrive on routine and predictability. Stick to a regular meal, walk, and playtime schedule to create a sense of stability and harmony.
- 5. Pawsitive Reinforcement Fiesta: Reward desired behaviors with love, treats, and praise. Positive reinforcement training encourages good manners and strengthens your bond with your fur baby.
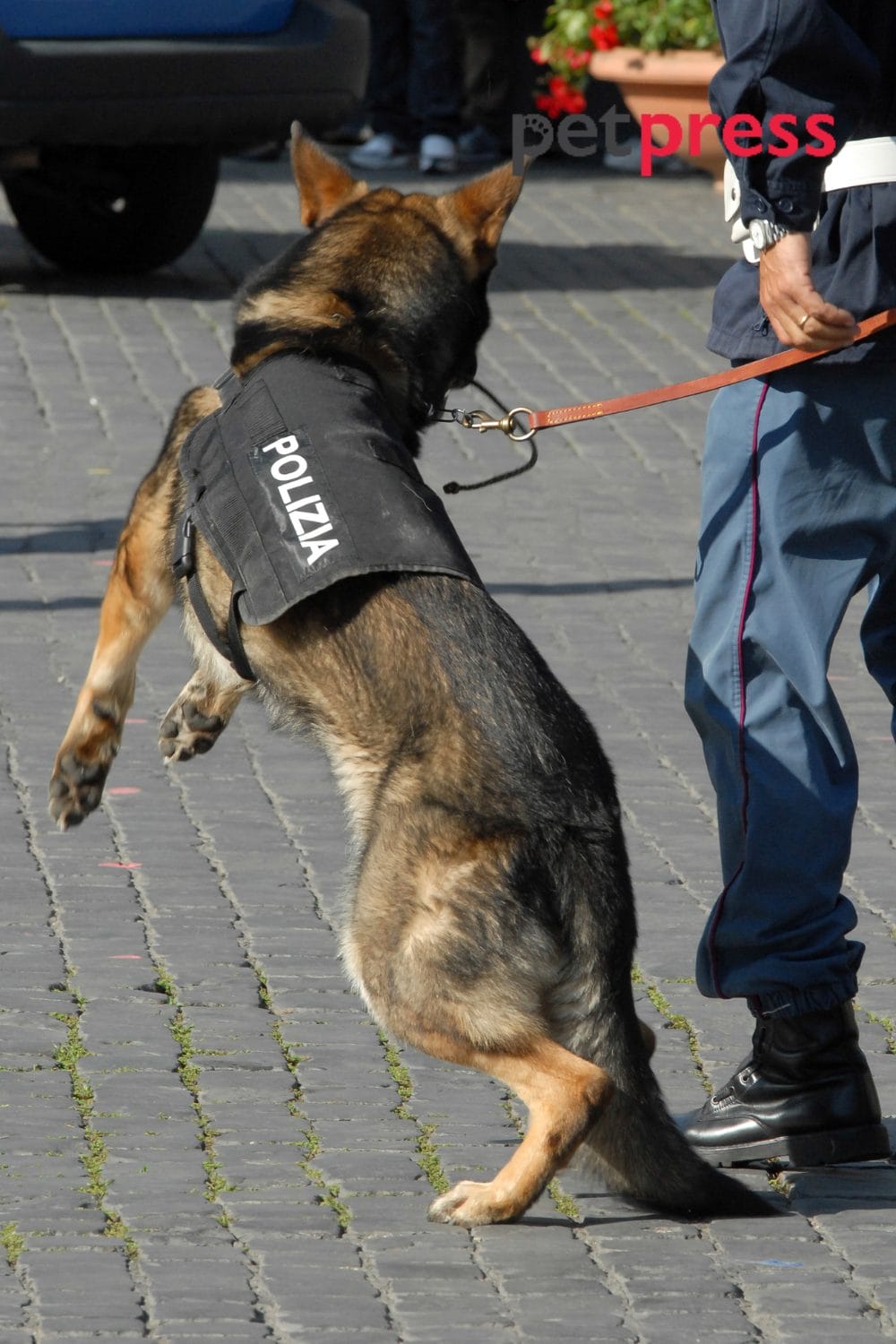

Seeking Professional Help
If your dog’s territorial aggression persists or worsens despite your efforts, it’s best to seek professional help. Trainers and behaviorists specialize in addressing complex issues and can offer personalized guidance for your dog’s needs.
Professional intervention for territorial aggression in dogs can make a huge difference. Don’t hesitate to ask for assistance; a harmonious relationship with your furry friend is worth it!
A certified dog trainer or behaviorist understands canine behavior and can identify subtle cues that an untrained eye may miss. They can create a personalized training plan based on your dog’s temperament, history, and triggers.
This targeted approach increases the chances of success in mitigating aggressive behavior. Moreover, these experts can teach practical techniques to reinforce appropriate behavior and manage situations that might trigger territorial aggression.
They also provide ongoing support and adjustments to the training plan, ensuring the strategies remain effective. Ultimately, seeking professional help can foster a healthier, happier relationship between you and your dog.
Conclusion: Managing Territorial Aggression in Dogs
Territorial aggression in dogs is an innate behavior that can be efficiently managed and potentially prevented through comprehensive understanding and effective techniques.
One can adeptly navigate this prevalent issue by recognizing behavioral cues, addressing root causes, implementing positive reinforcement training, fostering a harmonious environment, and seeking professional assistance while strengthening the bond with one’s canine companion.
If you found this post helpful and crave a deeper understanding of the captivating realm of dog behavior, be sure not to overlook our related article! It’s a must-read for every dog owner, with invaluable insights and practical tips. Don’t hesitate; unlock your knowledge today!

FAQs: The Most Common Questions About Territorial Aggression in Dogs
Territorial aggression can stem from various factors, including genetics, lack of socialization, fear, trauma, or a desire to protect their owners.
Proper socialization, positive reinforcement training, and a balanced environment with consistent boundaries can help prevent or minimize territorial aggression.
Territorial aggression is a common behavioral issue in dogs, but it can be managed effectively with the right approach and training.
While territorial aggression may not be entirely cured, it can be significantly reduced through consistent training, behavior modification, and addressing underlying triggers.
Certain dog breeds, like guard dogs or herding breeds, may have a higher tendency for territorial behavior due to their historical roles. However, any dog can exhibit territorial aggression due to personality, socialization, and environment.
Related Post:
How to Stop Dog Aggression Towards Other Pets
- Does Cat Litter Melt Ice? The Complete Guide to Winter Safety - January 30, 2026
- Happy Tail Dogs: Understanding This Common Canine Condition - January 29, 2026
- How Cold Can Outdoor Cats Handle? Feline Winter Safety - January 27, 2026


GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings